Comparison Operators:
Evaluating condition
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | (Equal to) is an assignment operator, which sets the variable on the left of the = to the value of the expression that is on its right. This operator assigns lvalue to rvalue. |
| == | (Double equals ) is a comparison operator, which transforms the operands having the same type before comparison. |
| === | (Triple equals) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, which returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. This operator performs type casting for equality. If we compare 2 with “2” using ===, then it will return a false value. |
| != | (Is not equal to) Returns true if the operands are not equal. |
| !== | (Strict not equal to) Returns true if the operands are of the same type but not equal, or are of different type. |
| > | (Greater than to) Returns true if the left operand is greater than the right operand. |
| < | (Less than to) Returns true if the left operand is less than the right operand |
| >= | (Greater than or equal to) Returns true if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand. |
| <= | (Less than or equal) Returns true if the left operand is less than or equal to the right operand. |
Logical operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| && | (Logical AND ) Returns expr1 if it can be converted to false; otherwise, returns expr2. Thus, when used with Boolean values, && returns true if both operands are true; otherwise, returns false. |
|| |
(Logical OR ) Returns expr1 if it can be converted to true; otherwise, returns expr2. Thus, when used with Boolean values, returns true if either operand is true; if both are false, returns false. |
| ! | (Logical NOT ) Returns false if its single operand that can be converted to true; otherwise, returns true. |
This table shows the results of the comparison operations

## Loop counters
- For loop
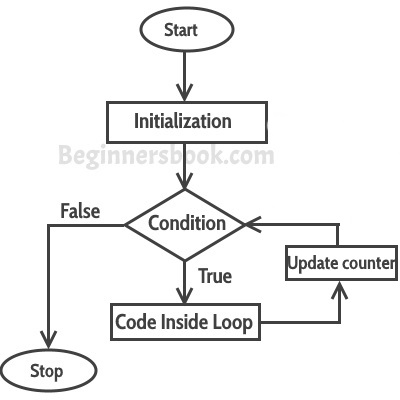
The JavaScript for loop statement allows you to create a loop with three optional expressions. The following illustrates the syntax of the for loop statement:
for (initialization; condition; post-expression) { // statements }.
-
Initialization
The initialization expression initializes the loop. The initialization expression is executed only once when the loop starts. You typically use the initialization is to initialize a counter variable.
- condition
The condition is an expression that is evaluated once before every iteration. The statement inside the loop is executed only when the condition evaluates to true.
-
post-expression
The for loop statement also evaluates the post-expression after each loop iteration. Generally, you use the post-expression to update the counter variable. The following flowchart illustrates.
 2.While loop
The following illustrates the syntax of the While loop statement:
while(condition expression)
{
/* code to be executed
till the specified condition is true */
}
2.While loop
The following illustrates the syntax of the While loop statement:
while(condition expression)
{
/* code to be executed
till the specified condition is true */
}
Example: while loop
var i =0; while(i < 5) { console.log(i); i++; }

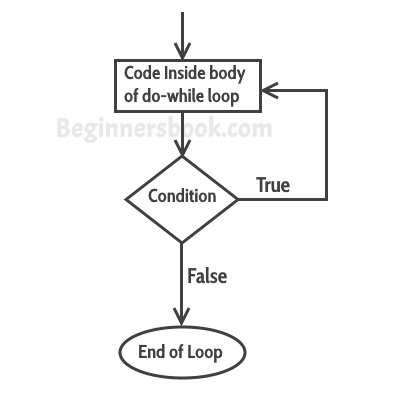
- Do while Loop JavaScript includes another flavour of while loop, that is do-while loop. The do-while loop is similar to while loop the only difference is it evaluates condition expression after the execution of code block. So do-while loop will execute the code block at least once. The following illustrates the syntax of the Do while loop statement: do{ / /code to be executed }while(condition expression)
Example:Do while Loop
var i = 0; do{ alert(i); i++; } while(i < 5)
I HOPE THAT IS CLEAR