Message Queues

A message queue is a queue of messages sent between applications. It includes a sequence of work objects that are waiting to be processed. … Another application, called a consumer, connects to the queue and gets the messages to be processed. Messages placed onto the queue are stored until the consumer retrieves them.
What does it mean that web sockets are bidirectional? Why is this useful?
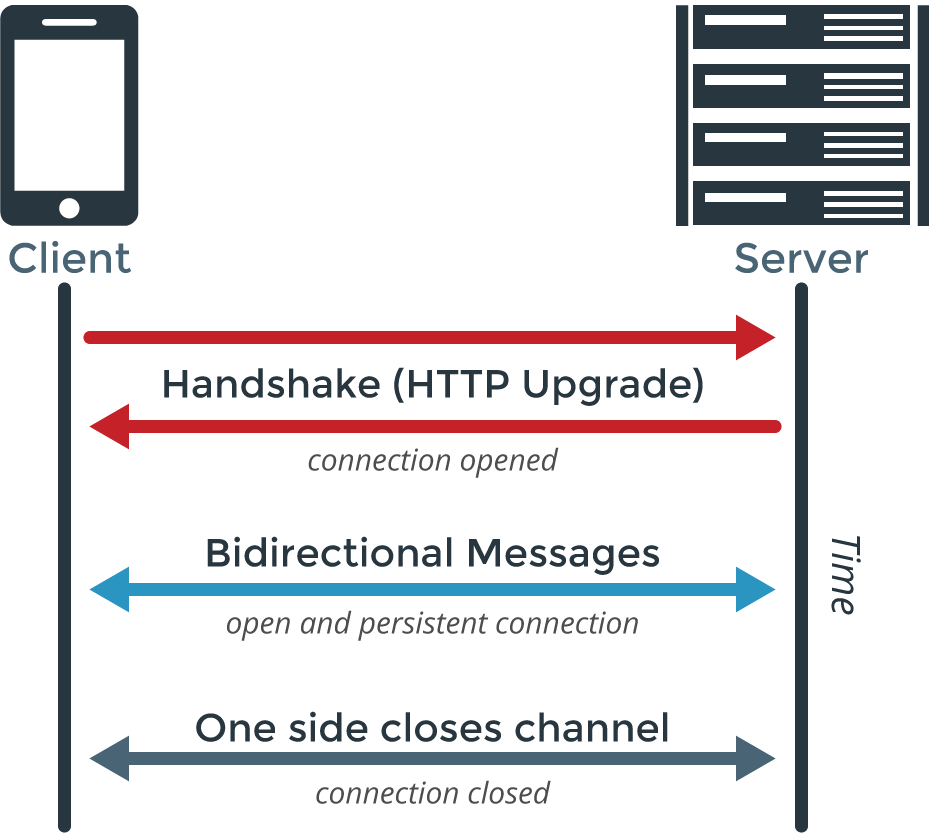
Whereas HTTP relies on a client request to receive a response from the server for every exchange, WebSockets allow for full-duplex bidirectional communication. This enables the server to send real-time updates asynchronously, without requiring the client to submit a request each time.
Does socket.io use HTTP? Why?
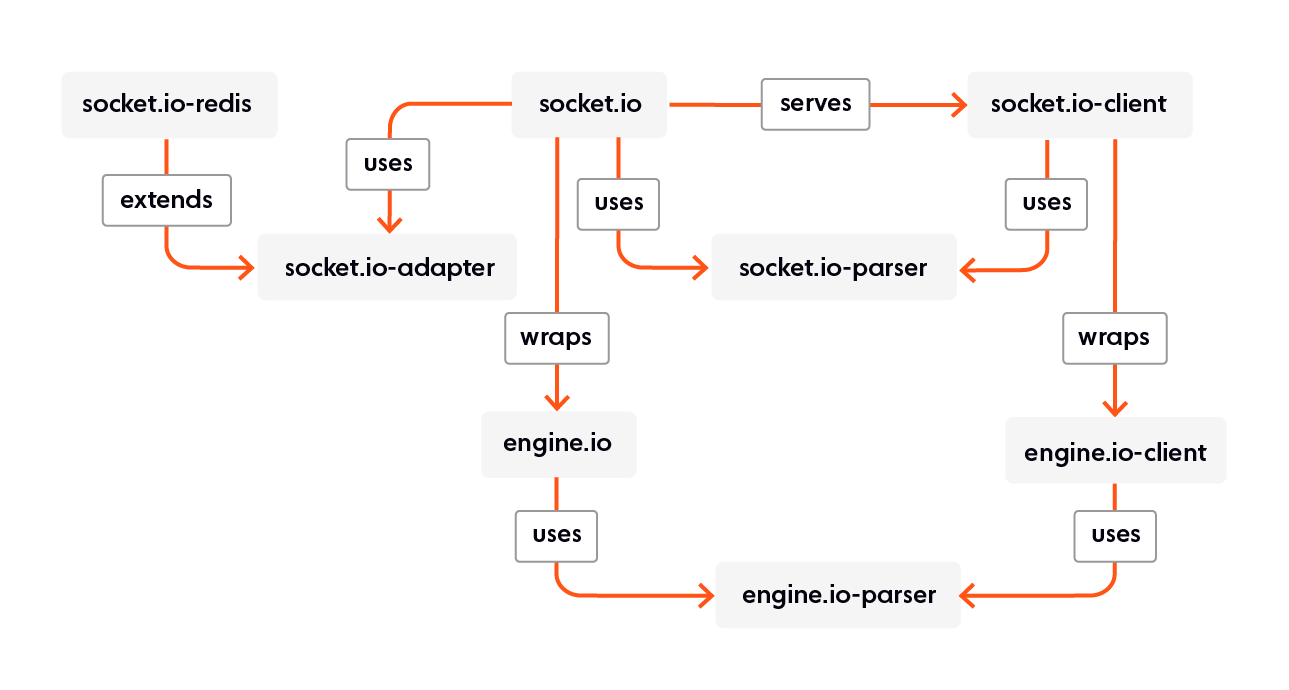 Even when websockets can be used, the initial connection setup it done over HTTP. Also, a socket.io server will attach to an HTTP server so it can serve its own client code through /socket.io/socket.io.js
Even when websockets can be used, the initial connection setup it done over HTTP. Also, a socket.io server will attach to an HTTP server so it can serve its own client code through /socket.io/socket.io.js
What happens when a client emits an event?

What happens when a server emits an event?
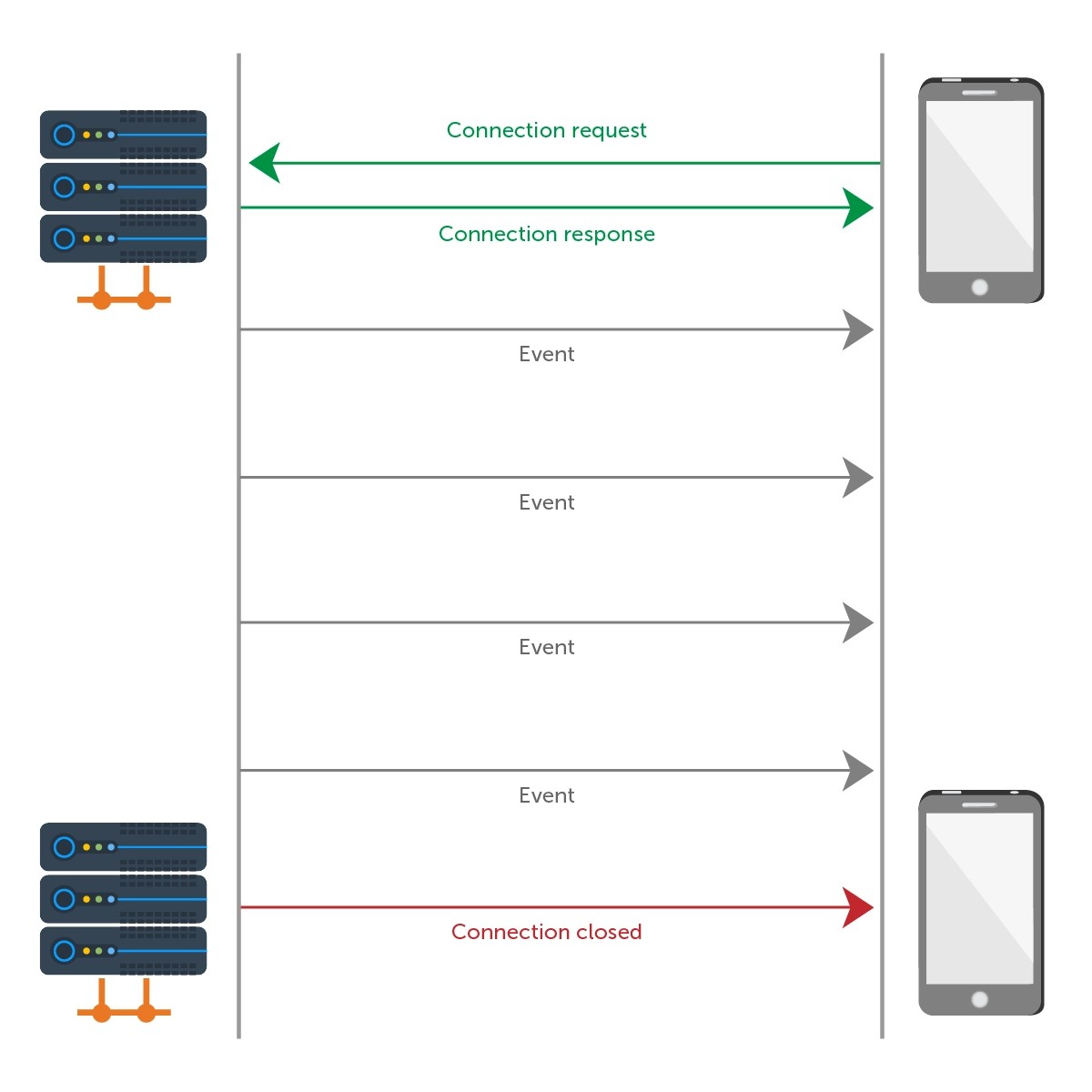
What happens if a client “misses” an event
SignalR will buffer at least the last 1000 messages sent to a given connectionId. This means that when you send the 1251st message, the first 250 get dereferenced by the buffer. This explains why when a client first connects to the server, it receives the entire sequence of messages. You have to send at least 1251 messages to a given client before the buffer will drop fragments. Again, this is all assuming default settings.
How can we mitigate this?

| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Socket | A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network. A socket is bound to a port number so that the TCP layer can identify the application that data is destined to be sent to. |
| Every TCP connection can be uniquely identified by its two endpoints | |
| Web Socket | The WebSocket API is an advanced technology that makes it possible to open a two-way interactive communication session between the user’s browser and a server. With this API, you can send messages to a server and receive event-driven responses without having to poll the server for a reply |
| Socket.io | Socket.IO allows bi-directional communication between client and server. Bi-directional communications are enabled when a client has Socket.IO in the browser, and a server has also integrated the Socket.IO package. … Engine.IO is used for the server implementation and Engine. IO-client is used for the client |
| Client | noun. a person or group that uses the professional advice or services of a lawyer, accountant, advertising agency, architect, etc. a person who is receiving the benefits, services, etc., of a social welfare agency, a government bureau, etc. a customer. anyone under the patronage of another; a dependent. |
| Server | A server is a computer or system that provides resources, data, services, or programs to other computers, known as clients, over a network. … An individual system can provide resources and use them from another system at the same time. This means that a device could be both a server and a client at the same time |
| OSI Model | The OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection Model) is a conceptual framework used to describe the functions of a networking system. The OSI model characterizes computing functions into a universal set of rules and requirements in order to support interoperability between different products and software |
| TCP Model | The TCP/IP model consists of five layers: the application layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer and physical layer. … TCP/IP is a hierarchical protocol made up of interactive modules, and each of them provides specific functionality |
| TCP | TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol a communications standard that enables application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network. It is designed to send packets across the internet and ensure the successful delivery of data and messages over networks |
| UDP | UDP is commonly used for applications that are “lossy” (can handle some packet loss), such as streaming audio and video. It is also used for query-response applications, such as DNS queries |
| Packets | In networking, a packet is a small segment of a larger message. Data sent over computer networks*, such as the Internet, is divided into packets. These packets are then recombined by the computer or device that receives them. … *A network is a group of two or more connected computers |