Trees
There are some people who come into your life and they are like branches on a tree. They are stronger than leaves, but you have to be careful with them. They will stick around through most seasons, but if you go through a storm or two in your life it’s possible that you could lose them.
Tree depth is a measure of how many splits a tree can make before coming to a prediction. This process could be continued further with more splitting until the tree is as pure as possible. The problem with many repetitions of this process is that this can lead to a very deep classification tree with many nodes.
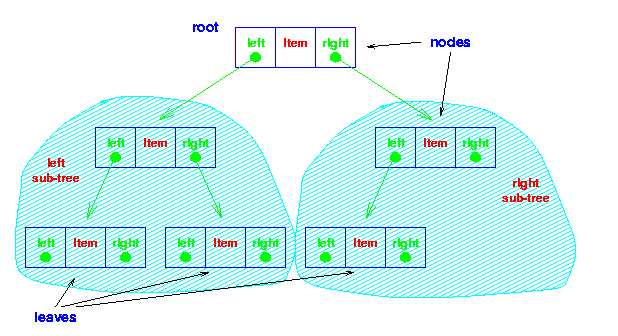
A tree is a hierarchical data structure defined as a collection of nodes. Nodes represent value and nodes are connected by edges. A tree has the following properties: The tree has one node called root


-
Node
A node is a fundamental part of a tree. It can have a name, which we call the “key.” A node may also have additional information. We call this additional information the “payload.” While the payload information is not central to many tree algorithms, it is often critical in applications that make use of trees.
-
Edge
An edge is another fundamental part of a tree. An edge connects two nodes to show that there is a relationship between them. Every node (except the root) is connected by exactly one incoming edge from another node. Each node may have several outgoing edges.
-
Root
The root of the tree is the only node in the tree that has no incoming edges. In Figure Figure 2, / is the root of the tree.
-
Path
A path is an ordered list of nodes that are connected by edges. For example, Mammal →
-
Carnivora → Felidae → Felis →
Domestica is a path.
-
Children
The set of nodes c
that have incoming edges from the same node to are said to be the children of that node. In Figure Figure 2, nodes log/, spool/, and yp/ are the children of node var/.
-
Parent
A node is the parent of all the nodes it connects to with outgoing edges. In Figure 2 the node var/ is the parent of nodes log/, spool/, and yp/.
-
Sibling
Nodes in the tree that are children of the same parent are said to be siblings. The nodes etc/ and usr/ are siblings in the filesystem tree.
-
Subtree
A subtree is a set of nodes and edges comprised of a parent and all the descendants of that parent.
-
Leaf Node
A leaf node is a node that has no children. For example, Human and Chimpanzee are leaf nodes in Figure 1.
-
Level
The level of a node n is the number of edges on the path from the root node to n
. For example, the level of the Felis node in Figure 1 is five. By definition, the level of the root node is zero.
-
Height
The height of a tree is equal to the maximum level of any node in the tree. The height of the tree in Figure 2 is two.



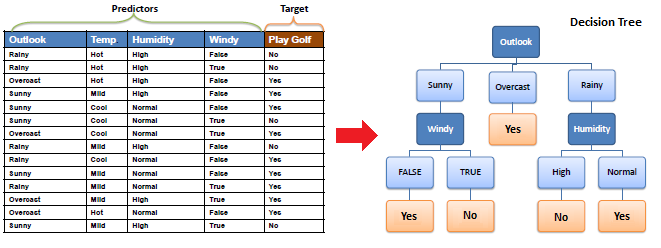 The ID3 algorithm builds decision trees using a top-down greedy search approach through the space of possible branches with no backtracking. A greedy algorithm, as the name suggests, always makes the choice that seems to be the best at that moment
The ID3 algorithm builds decision trees using a top-down greedy search approach through the space of possible branches with no backtracking. A greedy algorithm, as the name suggests, always makes the choice that seems to be the best at that moment

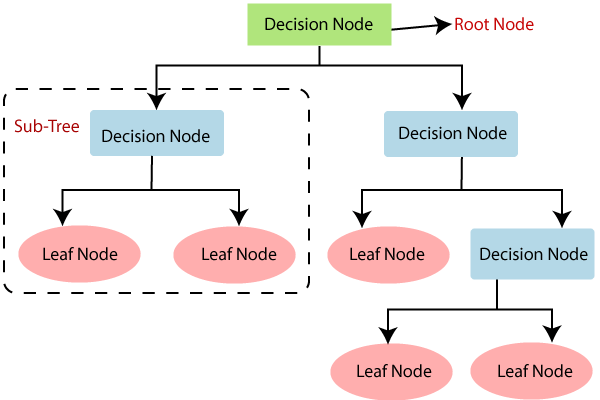
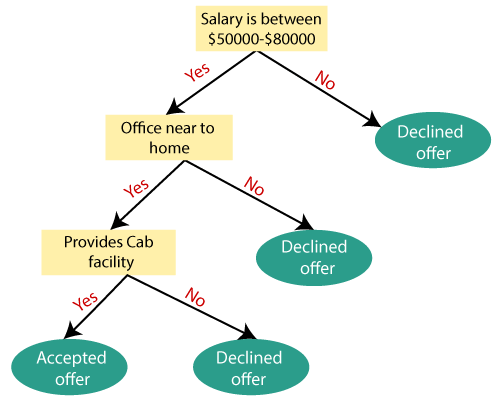
Decision Tree Analysis is a general, predictive modelling tool that has applications spanning a number of different areas. In general, decision trees are constructed via an algorithmic approach that identifies ways to split a data set based on different conditions. It is one of the most widely used and practical methods for supervised learning. Decision Trees are a non-parametric supervised learning method used for both classification and regression tasks. The goal is to create a model that predicts the value of a target variable by learning simple decision rules inferred from the data features.